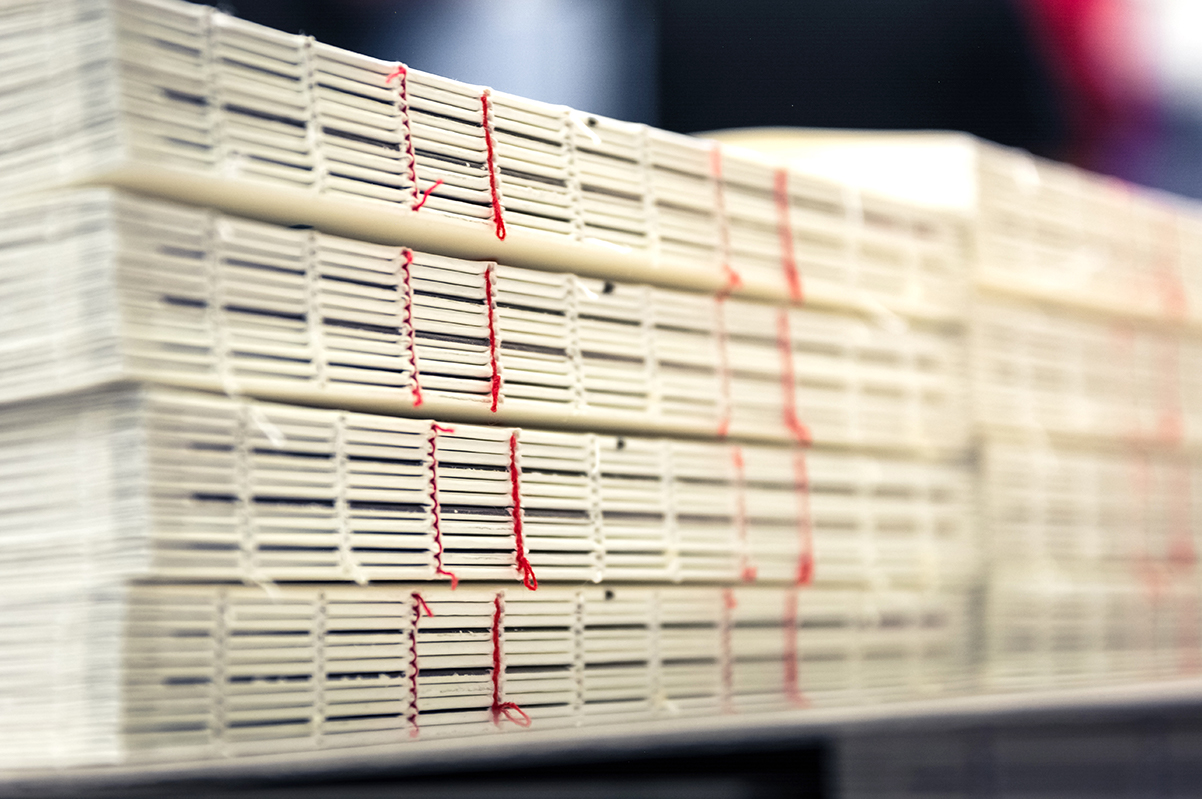
Whether glued, stapled or otherwise bound together, a proper binding turns a stack of sheets into a book, magazine or notepad. We present different binding types, from gluing to spiral binding, and explain how to choose the perfect binding for your printed product.
A comparison of binding types for printed matter
Bookbinding turns loose pages and folded sheets into a usable print product. There is a varied selection of binding types and not all bindings are equally well-suited for a given project. Production costs, durability, page count and the application of a printed product are the most important criteria for choosing a binding type. To make sure you pick the right binding for your requirements, this article will look into the most popular binding techniques and highlight their advantages and disadvantages. This will enable you to easily determine the correct binding type for your next creative project.
Contents
- Saddle stitch binding
- Perfect binding
- Glued fold binding
- Glued pad binding
- Thread sewn binding
- Spiral or wire binding
- More binding types
- Tip: How to choose the perfect binding type
- Table: Which binding for which product?
Saddle stitch binding
Saddle stitching, also called stapled binding, is a very popular and easy binding method in which pages are folded, creased and stapled together. It is often used for the following products:
- magazines
- different types of advertising material
- brochures
- catalogues
Saddle stitch binding refers to the bookbinding method in which folded sheets of paper are stapled together along the spine edge in one workflow. Usually, the wire is punched through the spine from the outside in two places and is bent flat on the inside. After it has been bound, the document is trimmed on three sides.
This binding method is both economical and quick. Moreover, it is highly durable and the pages open completely flat so that printed content is not lost in the gutter (the center of the printed product when opened).
Saddle stitch binding only works with page counts that can be divided by four; individual pages are not possible. Fold-in pages on the cover or inside pages are the only exception.

The maximum number of pages depends on the paper weight. The higher the paper weight, the fewer pages can be included. For comparison: A brochure can have 40 pages of 250 gsm coated art paper and 128 pages of the same paper in 90 gsm quality.
The wire used in saddle stitching is usually available in a selection of different colours. Loop stitch binding is a variant of this bookbinding method which involves loops provided along the external spine to file the document into a ring binder without the need for punched holes.
Pros and cons of saddle stitch binding
- Pros
- fast and cost-efficient
- durable
- opens flat
- eco-friendly thanks to low material consumption
- many formats and variations possible
- printed content not lost in the gutter
- loop stitch binding to file and archive documents
- Cons
- limited number of pages
- no superior appearance
- page creep
- not easily stackable
Perfect binding
With this bookbinding technique, the pages of a printed product are glued together to produce a durable result. Perfect binding is ideal for:
- sales catalogues
- magazines
- brochures with a high page count
- paperbacks
- advertising brochures
In perfect binding, sections of folded sheets are collated to form the inside of the printed product. Their spines are trimmed off and roughed up to improve bonding with the glue and the paper dust produced in this process is removed. Next, the glue is applied to the spine using rollers or nozzles and the wrap-around cover is pressed onto the still wet glue. Then the product is trimmed on three sides, and voilà, the perfect bound product is finished. This method uses either hot-melt or PUR adhesives.

Hot-melt adhesive, the more affordable solution, has limited durability and is therefore particularly well suited for simple and short-lived products.
Perfect binding with PUR adhesives cost more but are also more durable, making them ideal for long-lasting, superior prints and high page counts.
The spine must be at least several millimetres thick for perfect binding to be an option. Therefore, products with few pages and low paper weights are generally not eligible. But it is possible to include single pages and different papers in the inside section.
Pros and cons of perfect binding
- Pros
- fast and relatively cost-efficient
- easy to stack
- excellent durability of PUR adhesives
- single pages and different paper types can be combined in one product
- superior appearance
- many formats and variations possible
- Cons
- printed content is partially lost in the gutter
- pages tend to close back up
- minimum spine strength dependent on page count and paper weight
- 72 hours drying time for PUR adhesives
Glued fold binding
A low-priced binding method, a glued fold is used for simple advertising products when durability is not a priority. The number of pages is limited and no cover can be added. Typical fold-glued products include:
- leaflets with few pages
- advertising mail
- direct mail marketing
- inserts

This binding method uses glue that is applied to the crease lines. First the sheets are glued to each other, then folded and trimmed. Depending on the folding type, documents with eight, twelve and sixteen pages can be implemented via sheet-fed offset printing. We offset printing is suitable for longer print runs. The paper weight should range between 80 and 135 gsm. In addition to sheet-fed offset, this binding method is also used in web offset printing to produce cost-efficient print runs starting from about 50,000, usually via in line production (all steps of the manufacturing process take place on the same machine).
Pros and cons of glued fold binding
- Pros
- economical and quick
- relatively easy to open
- many formats and papers possible
- Cons
- low page count
- only for short-lived products
- no cover
- limited selection of paper weights
- combining different papers not possible
- no high-end appearance
Glued pad binding
This pad binding technique is both simple and economical. It is often used to bind short-lived print material to allow tearing out individual pages. This makes glued pad binding ideal for the following products:
- notepads and writing pads
- carbonless copy paper
- writeable desk pads
- training documents
- coupons, vouchers and event tickets

In glued pad binding, adhesive is applied to the spine only. First the sheets to be glued are trimmed. Assembling the individual sheets is only necessary if there are different designs within one pad and when offset printing is used. With digital printing, different designs are possible without collating the individual sheets. A stabilising chipboard backing and a cover can optionally be glued on the outside. To allow tearing out the sheets, low-tack adhesives are used.
Different paper types may be combined within one pad: Uncoated papers are particularly well suited. High paper weights and too many pages can cause premature glue failure and result in loose pages.
Pros and cons of pad gluing
- Pros
- single sheets can be torn out easily
- filing possible with punched holes
- low-priced
- different paper types possible for the inside
- various formats and variations
- Cons
- limited use of coated papers
- low durability
- Designs must not reach into the glued area.
- limited page count depending on the application
Thread sewn binding
A very strong and durable binding, thread sewn binding uses thread to sew sheets together. However, this binding method is more complex and therefore more expensive, making it ideal for high-quality publications. Typical products which are thread sewn include:
- illustrated books
- bibles
- art books
- fiction books
- catalogues
In thread sewn binding, individual sheets are folded first which are then assembled and sewn together. The resulting book block is glued on the spine and trimmed on three sides. Next the thread-sewn book block can be glued to the cover. Thread sewn binding allows a variety of covers (e.g. hard covers) to be implemented. The further processing thus depends on the type of cover.

To add colour, you can choose the colours of the endband or headband, bookmark and thread from a broad colour palette. Moreover, a wide selection of fabrics and materials is available for the cover and different paper stocks for the inside section. No other binding method is compatible with such a wide variety of different materials. Also, there are virtually no limits to the number of pages: More than 1,000 pages can be bound together with this long-lasting and stable binding technique.
Pros and cons of thread sewn binding
- Pros
- very sturdy and durable
- opens flat
- superior appearance
- a lot of pages can be bound with ease
- many variations possible
- Cons
- expensive
- Single pages cannot be included.
- Folded sheets must comprise four, eight or sixteen pages.
- Images over two pages partially get lost in the gutter.
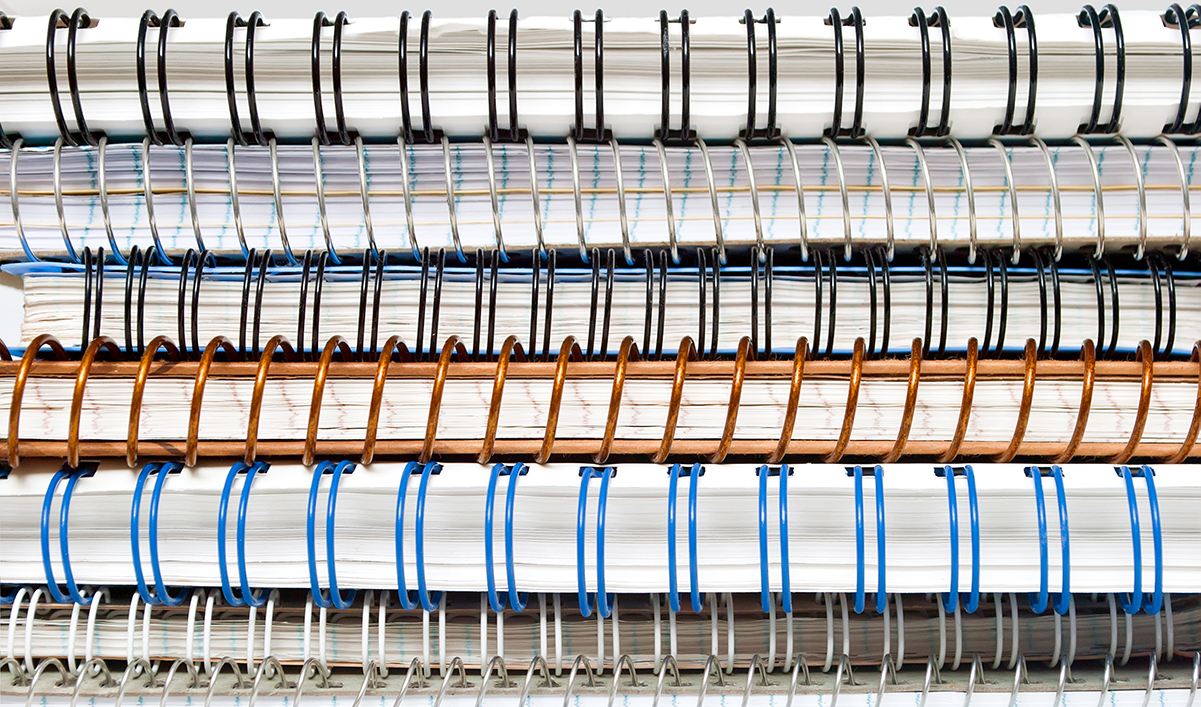
Spiral binding
This binding method is also known as twin loop, double loop, double-o, duo-wire or simply wire binding. It utilizes a wire or pre-formed pairs of wire loops which are inserted through holes that have been punched through the book’s cover and pages. Wire binding is very popular and is often used for the following products:
- calendars
- cookbooks and music books
- training manuals
- writing pads
- sales documents
- brochures
In spiral binding, holes are punched through the book’s cover and pages through which a wire or wire loops are inserted. The wire ends are folded in to prevent the sheets from getting loose.

No other bookbinding method opens as conveniently. The pages open flat and can even be turned over completely. The maximum number of pages depends on the spiral diameter and on the paper weight. With sufficiently large spiral diameters and low paper weights, several hundred pages are no problem. Different print substrates and individual sheets can be mixed in a spiral bound document. The spirals are available in different colours and materials. There is a gap when opening the pages, causing designs that run across the spine to be broken up.
Pros and cons of spiral binding
- Pros
- durable
- very easy to open
- pages can be turned over completely
- large page counts possible
- materials can be combined easily
- including single sheets
- Cons
- Designs that run across the spine are broken up.
- There is a gap between the opened pages.
- limited stackability due to the protruding spiral
- smaller type area because of punched holes
More binding types
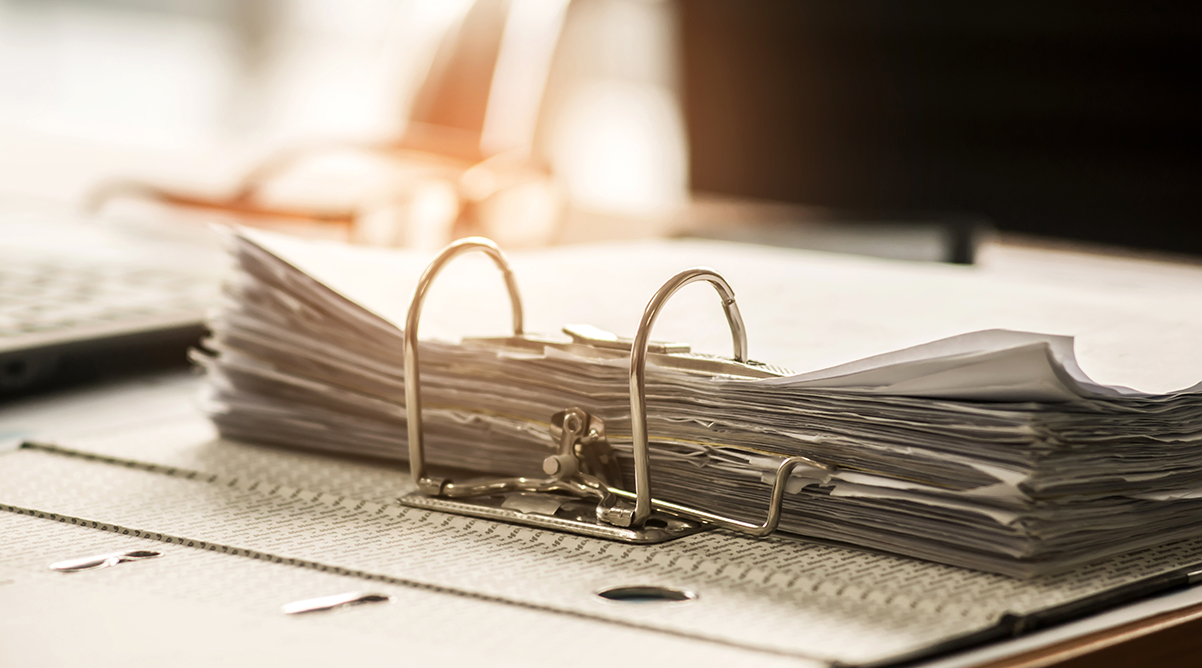
You want to hold together loose leaves with the option to add more pages at any time? Then lever arch files and binders are what you need. They are sturdy, the inserted sheets can be turned over and you can add more pages whenever you like.
Folders are another option to keep single documents secure in one place. Strictly speaking, this is no binding method as the sheets are held together loosely. Folders are available in different styles, for example, with tuck-in or glued flaps, different capacities, slots for business cards and pen holders. They are popular for events as well as sales and training documents.
Tip: How to choose the right binding type
To determine the ideal binding method for your creative project, you have to consider the following aspects:
- costs
- durability
- page count
- opening behaviour
- value/appearance
Other less important criteria include:
- stackability
- combining different paper types
- filing the sheets
- tearing out single sheets
- including single sheets
A selection guide
Now if you determine the most important factors for your project, you can conclude the suitable binding methods:
Example A
Your printed product should meet these criteria:
- low-priced
- medium durability
- medium page count (approx. 100 pages)
- opens flat
In this case, only two binding types are eligible, namely spiral binding and saddle stitch binding.
Example B
Your printed product should meet these criteria:
- high quality
- high page count (approx. 300 pages)
- opens flat
- excellent durability (many years)
To meet these requirements, only thread sewn binding will work.
Example C
Your printed product should meet these criteria:
- different paper types for the pages
- single sheets
- low page count (approx. 40 pages)
- high quality
- relatively low-priced
- low durability
With this combination of criteria, hot-melt adhesive binding is the method to go for.
When choosing the appropriate binding method, you therefore have to define the requirements for your printed product as exactly as possible.
Which binding to choose for which product?
The following table gives an overview of bound products at Onlineprinters with the available binding types.
| Saddle stitch binding | Hot-melt perfect binding | PUR perfect binding | Glued fold binding | Glued pad binding | Thread sewn binding | Spiral binding | |
| Brochures | × | × | × | ||||
| Catalogues | × | × | × | ||||
| Notepads | × | ||||||
| Carbonless copy paper | × | ||||||
| Event tickets | × | ||||||
| Sticky notes | × | ||||||
| Desk pads | × | ||||||
| Wall calendars | × | × | |||||
| Desk calendars | × | ||||||
| Hardcover books | × |
Credits
Title photo: zefart (via Shutterstock)
Other photos: Africa Studio (via Shutterstock), smolaw (via Shutterstock), kazoka (via Shutterstock), multifacetedgirl (via Pixabay), Hunter Bliss Images (via Shutterstock), pashminu (via Pixabay), Landysh (via Shutterstock), Tirachard Kumtanom (via Pexels), Moobin (via Shutterstock) and Onlineprinters GmbH